Cerebral Cortex
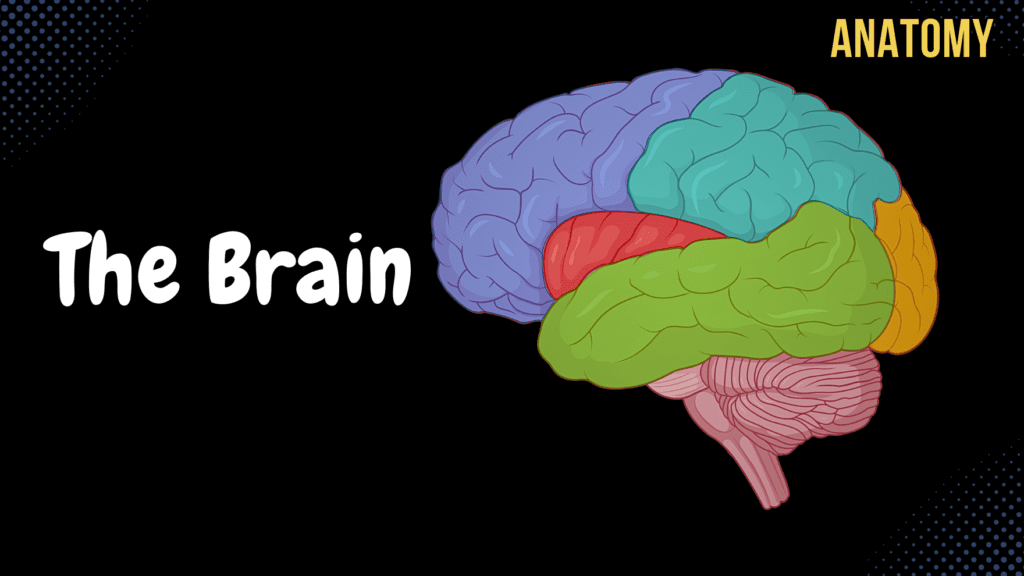
Cerebral Cortex (Function, Covering, Lobes, Sulcus, Gyrus, Fissures) Official Links Instagram Youtube Jki-discord Notes & Illustrations Quizzes Summary & Transcript Notes ☆ Members Only Go to PDF Notes Illustrations ☆ Members Only Go to Illustrations 12345678910 Cerebral Cortex – QUIZ Test your understanding with 10 random multiple-choice questions from the question bank. You're in the preview mode. Note: All elements work correctly on the front end. 1 / 10 The hippocampal formation is involved in which function? A) Language production B) Motor coordination C) Memory processing D) Visual processing It plays a critical role in memory encoding and retrieval. 2 / 10 What is the function of the prefrontal cortex? A) Decision-making and personality B) Auditory processing C) Vision D) Somatosensory input It is involved in decision-making, personality, and executive functions. 3 / 10 The calcarine sulcus is a landmark for which cortex? A) Gustatory cortex B) Primary motor cortex C) Primary visual cortex D) Primary auditory cortex The primary visual cortex (Brodmann Area 17) is located here. 4 / 10 The longitudinal fissure separates which structures? A) Parietal and occipital lobes B) Frontal and parietal lobes C) Left and right hemispheres D) Temporal and frontal lobes It divides the left and right cerebral hemispheres. 5 / 10 What is the function of the primary somatosensory cortex? A) Processes tactile sensations B) Controls voluntary motor movements C) Regulates emotions D) Processes auditory input Located in the postcentral gyrus, it processes tactile sensations. 6 / 10 Wernicke’s area is responsible for which function? A) Spatial awareness B) Language comprehension C) Voluntary motor control D) Speech production It is essential for language comprehension. 7 / 10 Which layer of the cerebral cortex contains pyramidal cells involved in motor output? A) External pyramidal layer B) External granular layer C) Molecular layer D) Internal pyramidal layer The internal pyramidal layer (layer 5) is responsible for motor output. 8 / 10 The parahippocampal gyrus is part of which lobe? A) Parietal lobe B) Occipital lobe C) Temporal lobe D) Frontal lobe It is part of the medial temporal lobe. 9 / 10 Which fissure separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes? A) Central sulcus B) Calcarine sulcus C) Longitudinal fissure D) Lateral fissure The lateral (Sylvian) fissure divides these lobes. 10 / 10 The calcarine sulcus is located in which lobe? A) Temporal lobe B) Parietal lobe C) Occipital lobe D) Frontal lobe It is found in the occipital lobe and is associated with the primary visual cortex. Your score is The average score is 0% Description Telencephalon Anatomy Pallium Cerebral Cortex White Matter of the Brain (Corpus Medullare Telencephali) Subpallium Basal Ganglion Functions of the Cerebral Cortex Thickness of 1.5-5mm Layers of the Cerebral Cortex Molecular Layer External Granular Layer External Pyramidal Layer Internal Granular Layer Internal Pyramidal Layer Multiform Layer Sensory Areas Primary Somatosensory Cortex Primary Visual Cortex Primary Auditory Cortex Motor Cortex Primary Motor Cortex Association Areas Surfaces of the Cerebral Hemispheres Medial Surface (Facies Medialis) Superiolateral Surface (Facies Superolateralis) Inferior Surface (Facies Inferior) Fissures of the Cerebral Hemispheres Longitudinal Fissure (Fissura Longitudinalis Cerebri) Transverse Fissure (Fissura Transversa Cerebri) Dural Septa Double layer of meningeal layer Falx Cerebri in the Longitudinal Fissure Tentorium Cerebelli in the Transverse Fissure of the Brain Falx Cerebelli Lobes of the Cerebral Hemispheres Frontal Lobe (Lobus Frontalis) Parietal Lobe (Lobus Parietalis) Temporal Lobe (Lobus Temporalis) Occipital Lobe (Lobus Occipitalis) Insular Lobe (Lobus Insularis) Main Sulci Lateral Sulcus (Sylvius) (Sulcus Lateralis) Central Sulcus (Rolando) (Sulcus Centralis) Parietooccipital Sulcus (Sulcus Parietooccipitalis) Frontal Lobe Precentral Sulcus (Sulcus Precentralis) Superior Frontal Sulcus (Sulcus Frontalis Superior) Inferior Frontal Sulcus (Sulcus Frontalis Inferior) Precentral Gyrus (Gyrus Precentralis) Primary Motor Cortex Motor Homunculus Corticospinal Tract Corticonuclear Tract (Corticobulbar Tract) Superior Frontal Gyrus (Gyrus Frontalis Superior) Middle Frontal Gyrus (Gyrus Frontalis Medius) Inferior Frontal Gyrus (Gyrus Frontalis Inferior) Broca’s Area (Motor Speech Center) Parietal Lobe Postcentral Sulcus (Sulcus Postcentralis) Intraparietal Sulcus (Sulcus Intraparietalis) Postcentral Gyrus (Gyrus Postcentralis) Primary Somatosensory Cortex Sensory Homunculus Superior Parietal Lobule (Lobulus Parietalis Superior) Inferior Parietal Lobule (Lobulus Parietalis Inferior) Supramarginal Gyrus Angular Gyrus Temporal Lobe Superior Temporal Sulcus (Sulcus Temporalis Superior) Inferior Temporal Sulcus (Sulcus Temporalis Inferior) Superior Temporal Gyrus (Gyrus Temporalis Superior) Primary Auditory Cortex Auditory Pathway Cochlear Nerve Cochlear Nuclei Lateral Lemniscus Inferior Colliculi Brachium of the Inferior Colliculi (Brachium Colliculi Inferior) Medial Geniculate Body Primary Auditory Cortex (Superior Temporal Gyrus) Wernicke’s Area Receptive Aphasia Middle Temporal Gyrus (Gyrus Temporalis Medius) Inferior Temporal Gyrus (Gyrus Temporalis Inferior) Medial Surface Cingulate Sulcus (Sulcus Cinguli) Subparietal Sulcus (Sulcus Subparietalis) Cingulate Gyrus (Gyrus Cinguli) Paracentral Sulcus (Sulcus Paracentralis) Marginal Sulcus (Sulcus Marginalis) Inferior Lobes and Gyri Olfactory Sulcus (Sulcus Olfactorius) Gyrus Rectus (Part of Prefrontal Cortex) Orbital Frontal Gyri (Gyri Orbitales) (Part of Prefrontal Cortex) Orbital Frontal Sulci (Sulci Orbitales) Insular Lobe (Lobus Insularis) Short Gyri of Insula (Gyri Breves Insulae) Long Gyrus of Insula (Gyrus Longus Insulae) Taste Sensation (Gustation Cortex) Visceral Sensation Vestibular Cortex Transcript Introduction0:03What’s up. Meditay here. Let’s continue the anatomy of the Central Nervous System.0:08In this segment, we’ll cover the anatomy of the Cerebral Cortex,0:11which is what we call the external Telencephalon.0:14So remember, the central nervous system consists of two parts:0:17the encephalon and the spinal cord. The encephalon is then further divided into specific parts.0:23We have the brainstem, which consists of the medulla, pons, and the midbrain0:27or the mesencephalon. We have the cerebellum back here, then the diencephalon and the Telencephalon.0:32Our focus in this video is going to be the telencephalon, which is this blue part here.0:37But If we change this picture into a little more realistic one,0:41we’ll find the spinal cord, the medulla, pons, and the Cerebellum. And then the Telencephalon0:46would be the whole blue area right here. Let’s now make a vertical section just like0:52this, cut it, and then look at the brain from this perspective. We’ll see this.0:56SO this is what we call a coronal section of the brain, and what we can see here is Pons and the1:02Midbrain, which are a part of the brainstem, and the
Diencephalon
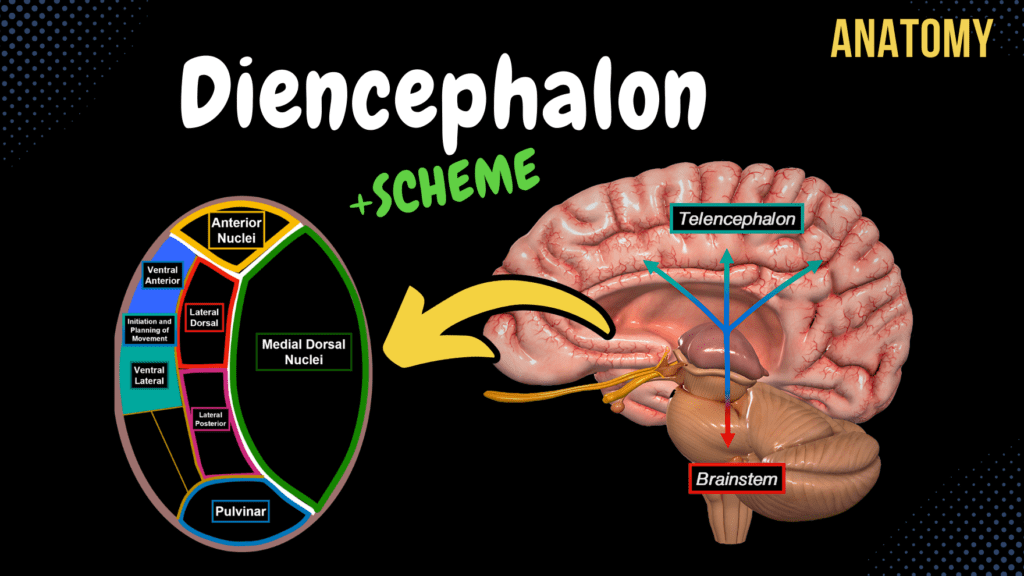
Diencephalon (Thalamus, Epithalamus, Subthalamus, Metathalamus, Hypothalamus) Official Links Instagram Youtube Jki-discord Notes & Illustrations Quizzes Summary & Transcript Notes ☆ Members Only Go to PDF Notes Illustrations ☆ Members Only Go to Illustrations 12345678910 Diencephalon – QUIZ Test your understanding with 10 random multiple-choice questions from the question bank. You're in the preview mode. Note: All elements work correctly on the front end. 1 / 10 Which structure produces cerebrospinal fluid in the third ventricle? A) Anterior nucleus of thalamus B) Mammillary bodies C) Choroid plexus D) Pineal gland The choroid plexus, located in the roof of the third ventricle, produces cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). 2 / 10 The lateral geniculate body of the thalamus receives input from which nerve? A) Optic nerve B) Vestibulocochlear nerve C) Trochlear nerve D) Trigeminal nerve The lateral geniculate body is part of the visual pathway, receiving input from the optic nerve (cranial nerve II). 3 / 10 Which nucleus of the hypothalamus regulates circadian rhythm through light input? A) Suprachiasmatic nucleus B) Arcuate nucleus C) Supraoptic nucleus D) Paraventricular nucleus The suprachiasmatic nucleus receives light information from the retina to regulate the circadian rhythm. 4 / 10 What structure connects the right and left thalami? A) Habenular commissure B) Optic chiasm C) Interthalamic adhesion D) Pineal gland The interthalamic adhesion structurally connects the two thalami across the third ventricle. 5 / 10 Which artery supplies the posterior thalamus? A) Vertebral artery B) Anterior cerebral artery C) Posterior cerebral artery D) Middle cerebral artery The posterior cerebral artery supplies the posterior thalamus, including the pulvinar and geniculate bodies. 6 / 10 The anterior nucleus of the thalamus is part of which circuit? A) Basal ganglia B) Optic pathway C) Papez circuit D) Reticular formation The anterior nucleus is part of the Papez circuit, associated with memory and emotional processing. 7 / 10 Which nucleus is primarily responsible for satiety? A) Lateral hypothalamic area B) Ventromedial nucleus C) Arcuate nucleus D) Supraoptic nucleus The ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus regulates feelings of satiety and inhibits hunger. 8 / 10 Which pathway connects the hippocampus to the mammillary bodies? A) Anterior commissure B) Habenular commissure C) Optic chiasm D) Fornix The fornix is a major fiber tract connecting the hippocampus to the mammillary bodies, important for memory. 9 / 10 Which part of the diencephalon is directly involved in the endocrine system? A) Hypothalamus B) Thalamus C) Subthalamus D) Epithalamus The hypothalamus regulates the pituitary gland and controls endocrine functions. 10 / 10 The medial geniculate body relays signals for which sensory system? A) Auditory B) Olfactory C) Visual D) Gustatory The medial geniculate body is part of the auditory pathway, relaying sound signals to the primary auditory cortex. Your score is The average score is 0% Description Topography of the Diencephalon Lies above the Mesencephalon Lies around the 3rd ventricle Parts of the Diencephalon Thalamus Epithalamus Subthalamus Metathalamus Hypothalamus External Thalamus Anterior Tubercle (Tuberculum Anterius Thalami) Pulvinar (Pulvinar Thalami) Interthalamic Adhesion (Adhesio Interthalamica) Internal Thalamus Internal Medullary Lamina (Medial Medullary Lamina) Anterior Nuclei Emotional Episodic Memory Part of the Limbic System (Hippocampus, Thalamus, Amygdala, Fornix, Cingulate Gyrus, Mamillary Body) Papez Circuit Medial Nuclei (Medial Dorsal Nucleus) Relates Sensory, Motor, and Olfactory with Emotions Lateral Nuclei Lateral Dorsal Lateral Dorsal Lateral Posterior Lateral Ventral Ventral Anterior (Basal Ganglia) Ventral Lateral (Basal Ganglia) VentroPosterioLateral Nuclei (VPL) Medial Lemniscus Spinothalamic Tract VentroPosterioMedial Nuclei (VPM) Trigeminal Lemniscus (Lemniscus Trigeminalis) Gustation (Taste) Pulvinar Metathalamus Medial Geniculate Body Auditory Pathway Cochlear Nerve Cochlear Nuclei Lateral Lemniscus Inferior Colliculi Brachium of the Inferior Colliculi (Brachium Colliculi Inferior) Medial Geniculate Body Primary Auditory Cortex (Superior Temporal Gyrus) Lateral Geniculate Body Visual Pathway Receptors of Optic Nerve (CNII) Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Body (Metathalamus) Primary Visual Cortex Brachium of the Superior Colliculi (Brachium Colliculi Superior) Inferior Colliculi Metathalamus Connection with Thalamus Pulvinar, Lateral Posterior, and Lateral Dorsal Receives information from Superior Colliculus and Inferior Colliculus Receives input from Medial Geniculate Body and Lateral Geniculate Body Epithalamus Pineal Gland (Corpus Pineale) Produces Melatonin Habenular Trigone (Trigonum Habenulae) Habenular Nuclei (Nuclei Habenulares) Habenular Commissure (Commissura Habenularum) Posterior Commissure (Commissura Posterior) Subthalamus Part of the Basal Ganglia Helps start, stop, and coordinate movement Hypothalamus Thalamus Opticus Optic Chiasm (Chiasma Opticum) Optic Tract (Tractus Opticus) Mamillary Bodies (Corpus Mamillare) Emotional Episodic Memory Reflexes with Olfaction Hypothalamic Nuclei Lateral Hypothalamic Area Posterior Hypothalamic Area Anterior Hypothalamic Area Paraventricular Nucleus (Pain) Preoptic Nucleus (Decreases HR, BP, etc.) Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (Circadian Rhythm) Supraoptic Nucleus (Thirst) Arcuate Nucleus (Regulates Hormone Release) Ventromedial Nucleus (Satiety Feeling) Mamillary Bodies Dorsal Medial (Sleep regulation and food intake) Tuber Cinerum Infundibulum Pituitary Gland (Posterior Pituitary) Sources used in this video Memorix Anatomy 2nd Edition by Hudák Radovan (Author), Kachlík David (Author), Volný Ondřej (Author) Biorender University notes and lectures Transcript Introduction0:01What’s up.0:03Meditay here.0:05Let’s continue the anatomy of the Central Nervous System.0:08In this segment, we’ll cover the complete anatomy of the different parts of the Diencephalon.0:13So the central nervous system consists of two parts: the encephalon and the spinal cord.0:18The encephalon is then further divided into specific parts.0:22We have the brainstem, which consists of the medulla, pons, and the Midbrain or the mesencephalon.0:27We have the cerebellum back here, then the Diencephalon and the telencephalon.0:31Our focus in this video is going to be the Diencephalon, which is here.0:35So in this video, we’re first going to look at the topography of the Diencephalon.0:39Basically, understand where is it?0:42What parts are considered the Diencephalon?0:44And what’s the orientation between these parts?0:46After that, we will cover the actual anatomy of all the structures that make up the Diencephalon.0:51But let’s orientate and understand their relationship first before doing so.Topography of Diencephalon0:57Alright.0:58Here you see Pons, Medulla, Cerebellum, and the Spinal Cord.1:02And if we remove one side of the hemisphere, we’ll be able to see the Midbrain.1:07And right above the Midbrain, we have our Diencephalon.1:10So the Diencephalon is a group of nerve nuclei that surrounds the Third Ventricle.1:15SO let’s repeat the ventricular system a little bit.1:18I’m sure you remember the fourth Ventricle, which continues down
Cerebellum
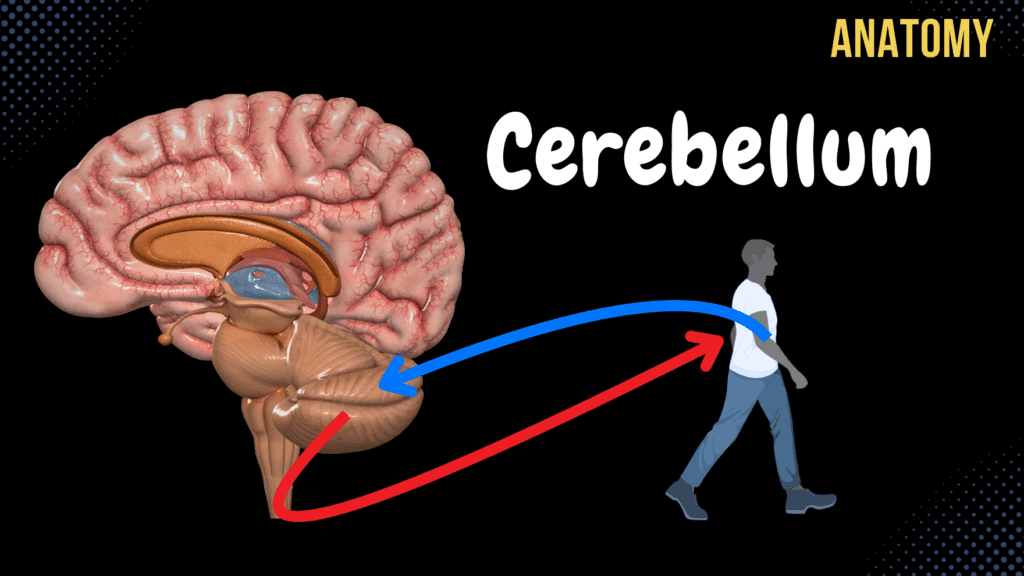
Cerebellum (External & Internal Structures, Tracts, Nuclei) Official Links Instagram Youtube Jki-discord Notes & Illustrations Quizzes Summary & Transcript Notes ☆ Members Only Go to PDF Notes Illustrations ☆ Members Only Go to Illustrations 12345678910 Cerebellum – QUIZ Test your understanding with 10 random multiple-choice questions from the question bank. You're in the preview mode. Note: All elements work correctly on the front end. 1 / 10 Which functional division of the cerebellum is associated with planning voluntary movements? A) Archicerebellum B) Vestibulocerebellum C) Neocerebellum D) Spinocerebellum The neocerebellum (cerebrocerebellum) is involved in planning, fine-tuning, and coordinating voluntary motor movements. 2 / 10 What is the main function of the dentate nucleus? A) Posture B) Fine motor coordination C) Balance D) Axial coordination The dentate nucleus coordinates voluntary motor activities and fine movements. 3 / 10 Which nucleus in the cerebellum is associated with the vestibulocerebellum? A) Dentate nucleus B) Emboliform nucleus C) Globose nucleus D) Fastigial nucleus The fastigial nucleus processes input from the vestibulocerebellum to maintain balance and control eye movements. 4 / 10 Which layer of the cerebellar cortex contains the Purkinje cells? A) Purkinje cell layer B) Granular layer C) Molecular layer D) None of the above The Purkinje cell layer is a single row of cells between the molecular layer and granular layer. 5 / 10 What fibers provide input to the inferior cerebellar peduncle? A) Trigeminal lemniscus B) Vestibulocerebellar fibers C) Anterior spinocerebellar fibers D) Corticospinal fibers The inferior cerebellar peduncle receives input from the vestibulocerebellar, posterior spinocerebellar, and olivocerebellar tracts. 6 / 10 Which pathway carries cerebellar output to the motor cortex? A) Vestibulospinal tract B) Corticobulbar tract C) Corticospinal tract D) Rubrospinal tract Cerebellar output reaches the motor cortex via the superior cerebellar peduncle, thalamus, and corticospinal tract. 7 / 10 What is the clinical significance of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA)? A) Drains blood B) Supplies inferior cerebellum C) None of the above D) Provides sensory input PICA supplies the inferior surface, vermis, and medulla. Its occlusion can lead to vertigo, dysphagia, and ataxia. 8 / 10 What is the main function of the anterior lobe of the cerebellum? A) Vestibular balance B) Coordination C) Muscle tone D) Fine movements The anterior lobe of the cerebellum is primarily responsible for regulating muscle tone and posture. 9 / 10 What is the clinical presentation of damage to the flocculonodular lobe? A) Truncal ataxia and nystagmus B) Fine tremors C) Spastic gait D) Hemiparesis Damage to the flocculonodular lobe leads to truncal ataxia and nystagmus due to its role in balance and eye movement coordination. 10 / 10 Which structure connects the cerebellum to the brainstem? A) Cerebellar peduncles B) Vermis C) Fissura Prima D) Arbor Vitae The cerebellar peduncles connect the cerebellum to the brainstem, facilitating communication with other parts of the CNS. Your score is The average score is 0% Description Topography of the Cerebellum Lies behind the Brainstem Cerebellum Function Smoothens Movement of Muscles Coordinates Balance and Posture Tone of Muscles – Passive Contraction of muscles External Structures of the Cerebellum Hemispheres of Cerebellum Vermis of Cerebellum Sulci of Cerebellum (Sulci Cerebelli) Folia of Cerebellum (Folia Cerebelli) Primary Fissure (Fissura Prima) Anterior Lobe of Cerebellum (Lobus Cerebelli Anterior) Posterior Lobe of Cerebellum (Lobus Cerebelli Posterior) Posterolateral Fissure (Fisura Posterolateralis) Flocculonodular Lobe (Lobus Flocculonodularis) Cerebellar Peduncles Superior Cerebellar Peduncle Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle Internal Structures of the Cerebellum Gray Matter of Cerebellum Cerebellar Cortex (Cortex Cerebelli) Dentate Nucleus (Nucleus Dentatus) Fastigial Nucleus (Nucleus Fastigii) Vestibulocerebellar Tract Globose Nucleus (Nucleus Globosus) Emboliform Nucleus (Nucleus Emboliformis) Spinocerebellar Tract White Matter of the Cerebellum Tree of Life (Arbor Vitae) Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle Vestibulocerebellar Tract Posterior Spinocerebellar Tract External Arcuate Fibers (Fibrae Arcuatae Externae) of Cuneate and Gracile Fascicle Olivocerebellar Tract (Tractus Olivocerebellaris) Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Pontocerebellar Tract from Corticocerebellar Tract Superior Cerebellar Peduncle Anterior Spinocerebellar Tract Sources used in this video Memorix Anatomy 2nd Edition by Hudák Radovan (Author), Kachlík David (Author), Volný Ondřej (Author) Biorender University notes and lectures Transcript Introduction0:01What’s up.0:03Meditay here.0:05Let’s continue the anatomy of the Central Nervous System.0:08In this segment, we’ll cover the anatomy of the Cerebellum0:11So the central nervous system consists of two parts: the encephalon and the spinal cord.0:16The encephalon is then further divided into specific parts.0:20We have the brainstem, which consists of the Medulla, Pons, and the Midbrain of the mesencephalon.0:25We have the Cerebellum back here, then the diencephalon and the telencephalon.0:30Our focus in this video is going to be the Cerebellum.0:33So in this video, we’re first going to cover the topography of the Cerebellum.0:38Then we’re gonna talk about the functions of it.0:41After that, we’ll go ahead and take a look at the external surface, and then make a cross-section0:45and look at the internal surface of the Cerebellum.0:48Basically covering the gray matter nuclei and the white matter tracts.Topography of the Cerebellum0:52Alright, so we can start by replacing this picture with a more realistic one.0:57From here, we’re able to see Pons, Medulla, Cerebellum, and the Spinal Cord.1:02And if we remove half of the cerebral hemisphere, we’ll see the rest of the brainstem, which1:07is the Midbrain.1:08So the Cerebellum mainly lies *behind* Pons and the Midbrain, as you see here.Functions of the Cerebellum1:14Now, what are the functions of the cerebellum?1:17When you’re walking, the Cerebellum continuously receives unconscious proprioception from muscles1:23and joints, as well as receiving information from different senses.1:28Based upon that, it sends out motor fibers that regulate all the muscle contractions1:32necessary to perform your movements smoothly.1:35So by doing that, it coordinates your balance and posture.1:40It regulates the tone of your muscles by passively contracting the muscles to ensure joint stability.1:46And it also smoothens voluntary movements of muscles.1:49So when you write.1:50Here most of the fibers come from the cerebral cortex since this is a voluntary movement.1:55But these movements are able to be smooth and precise by the Cerebellum engaging its2:00fibers into the muscles necessary to stabilize the movements.2:04So these are the top three functions the Cerebellum has.External Structures of the Cerebellum2:09Let’s now finally understand the
Mesencephalon (Midbrain)
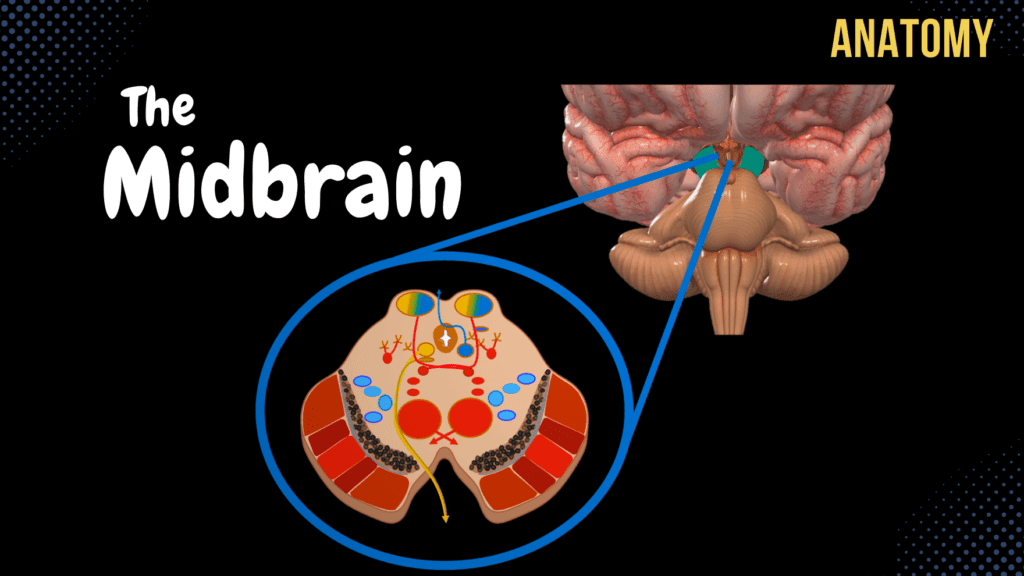
Mesencephalon (Midbrain) – External & Internal structures Official Links Instagram Youtube Jki-discord Notes & Illustrations Quizzes Summary & Transcript Notes ☆ Members Only Go to PDF Notes Illustrations ☆ Members Only Go to Illustrations 12345678910 Mesencephalon – QUIZ Test your understanding with 10 random multiple-choice questions from the question bank. You're in the preview mode. Note: All elements work correctly on the front end. 1 / 10 Which midbrain structure is involved in reflex control of balance and posture? A) Reticulospinal Tract B) Vestibulospinal Tract C) Rubrospinal Tract D) Corticospinal Tract The vestibulospinal tract originates in the brainstem, including the midbrain, to maintain balance and posture. 2 / 10 What part of the midbrain contains the corticospinal and corticopontine tracts? A) Cerebral Peduncles B) Red Nucleus C) Tegmentum D) Tectum The cerebral peduncles house the corticospinal and corticopontine tracts, which are involved in motor signal transmission. 3 / 10 Which midbrain structure is associated with the auditory pathway? A) Inferior Colliculus B) Lateral Lemniscus C) Medial Lemniscus D) Superior Colliculus The inferior colliculus processes auditory input and relays it to the medial geniculate body of the thalamus. 4 / 10 Which cranial nerve exits dorsally from the midbrain? A) Oculomotor Nerve B) Trochlear Nerve C) Trigeminal Nerve D) Abducens Nerve The trochlear nerve (CN IV) is the only cranial nerve to exit from the dorsal surface of the brainstem. 5 / 10 What is the function of the tectospinal tract originating in the superior colliculus? A) Voluntary Movement B) Auditory Reflex C) Visual Reflex Movement D) Pain Modulation The tectospinal tract coordinates head and neck movements in response to visual stimuli. 6 / 10 Which cranial nerve emerges between the cerebral peduncles of the midbrain? A) Abducens Nerve B) Trigeminal Nerve C) Trochlear Nerve D) Oculomotor Nerve The oculomotor nerve (CN III) emerges between the cerebral peduncles on the anterior surface of the midbrain. 7 / 10 The superior colliculus is connected to the primary visual cortex via which structure? A) Lateral Lemniscus B) Brachium of Superior Colliculus C) Medial Lemniscus D) Tectospinal Tract The brachium of the superior colliculus transmits visual signals to the primary visual cortex through the lateral geniculate body. 8 / 10 Which midbrain pathway connects the cochlear nuclei to the inferior colliculus? A) Spinothalamic Tract B) Lateral Lemniscus C) Trigeminal Lemniscus D) Medial Lemniscus The lateral lemniscus is part of the auditory pathway, transmitting signals from the cochlear nuclei to the inferior colliculus. 9 / 10 What structure in the midbrain relays motor information from the cerebellum to the thalamus? A) Tectum B) Lateral Lemniscus C) Substantia Nigra D) Red Nucleus The red nucleus integrates motor information from the cerebellum and relays it to the thalamus for coordination. 10 / 10 What is the tectum of the midbrain composed of? A) Tegmentum B) Cerebral Peduncles C) Superior and Inferior Colliculi D) Substantia Nigra The tectum of the midbrain includes the superior and inferior colliculi, which are involved in visual and auditory reflexes, respectively. Your score is The average score is 0% Description Topography of the Mesencephalon Lies above the Pons, Below Diencephalon, In front of the Cerebellum Anterior Surface Posterior Surface Anterior Surface of the Mesencephalon Cerebral Peduncles (Pedunculus Cerebri) Interpeduncular Fossa (Fossa Interpeduncularis) Posterior Perforated Substance (Substantia Perforata Posterior) Oculomotor Sulcus of Mesencephalon (Sulcus Nervi Oculomotorii) 3rd Cranial Nerve (Oculomotor nerve) Posterior View of the Mesencephalon Cerebral Peduncles (Pedunculus Cerebri) Tectal Plate (Lamina Tecti) Superior Colliculus (Colliculi Superior) Visual Pathway: Receptors of Optic Nerve (CNII) Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Body (Metathalamus) Primary Visual Cortex Brachium of the Superior Colliculi (Brachium Colliculi Superior) Inferior Colliculus (Colliculi Inferior) Auditory Pathway: Cochlear Nerve Cochlear Nuclei Lateral Lemniscus Inferior Colliculi Brachium of the Inferior Colliculi (Brachium Colliculi Inferior) Primary Auditory Cortex (Superior Temporal Gyrus) Lateral Sulcus of Mesencephalon (Sulcus Lateralis Mesencephali) Trigone of Lateral Lemniscus (Trigonum Lemnisci Lateralis) Trochlear Nerve (CN IV) Internal Surface of the Mesencephalon Tectum of Midbrain Tegmentum of Midbrain Cerebral Peduncles Gray Matter of Mesencephalon Red Nucleus (Nucleus Ruber) Corticopontine Tract Pontocerebellar Tract (Transverse Pontine Fibers) Cerebellorubral Tract Rubrospinal Tract Substantia Nigra Substantia Nigra pars Reticulata Substantia Nigra pars Compacta Part of Basal Ganglia (Putamen, Globus Pallidus, Caudate, Thalamus, Subthalamus, Striatum, Lentiform Nucleus) Helps Start Movement, Stop Movement, Modulate Movement Disease here causes Parkinson’s Disease and TRAP symptoms (Tremor, Rigidity, Akinesia, Postural Instability) Superior Colliculi Level: Nucleus of Oculomotor Nerve (Nuclei Nervi Oculomotorii) Posterior Accessory Nucleus of Oculomotor Nerve (Nucleus Accessorii Nervi Oculomotorii) Inferior Colliculi Level: Nucleus of Trochlear Nerve (Nuclei Nervi Trochlearis) Mesencephalic Nucleus of Trigeminal Nerve (Nucleus Mesencephalicus Nervi Trigemini) Periaqueductal Grey Substance (Substantia Grisea Centralis) Reticular Formation (Formatio Reticularis) White Matter of Mesencephalon Ascending Tracts Medial Lemniscus (Lemniscus Medialis) Gracile Fascicle (Fasciculus Gracilis) to Gracile Nucleus Cuneate Fascicle (Fasciculus Cuneatus) to Cuneate Nucleus Medial Lemniscus is formed through Internal Arcuate Fibers (Fibrae Arcuatae Internae) Epicritic Sensibility (Proprioception and Mechanoreceptors) Spinal Lemniscus (Lemniscus Spinalis) Anterior Spinothalamic Tract (Tractus Spinothalamicus Anterior) Lateral Spinothalamic Tract (Tractus Spinothalamicus Lateralis) Trigeminal Lemniscus (Lemniscus Trigeminalis) Anterior Spinocerebellar Tract (Tractus Spinocerebellaris Anterior) Lateral Lemniscus (Lemniscus Lateralis) from Cochlear Nerve Descending Tracts Vestibulospinal Tract (Tractus Vestibulospinalis) Rubrospinal Tract (Tractus Rubrospinalis) Tectospinal Tract (Tractus Tectospinalis) Posterior Tegmental Decussation (Decussatio Tegmentalis Posterior) Reticulospinal Tract (Tractus Reticulospinalis) Anterior Tegmental Decussation (Decussatio Tegmentalis Anterior) Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus (Fasciculus Longitudinalis Medialis) In the Cerebral Peduncles Corticospinal Tract (Tractus Corticospinalis) Corticonuclear Tract (Corticobulbar Tract) Corticopontine Tract (Tractus Corticopontineus) Frontopontine Tract Parietopontine Tract Temporopontine Tract Occipitopontine Tract Transcript Introduction 0:03 What’s up. Meditay here. Let’s continue the anatomy of the Central Nervous System. 0:08 In this segment, we’ll cover the complete anatomy of the Midbrain, also known as the mesencephalon 0:13 So remember, the central nervous system consists of two parts: 0:16 the encephalon and the spinal cord. The encephalon is then further divided into specific parts. 0:22 We have the brainstem, which consists of the Medulla, Pons, and the midbrain or the 0:26 mesencephalon. We have the cerebellum back here, then the Diencephalon and the telencephalon. 0:31 Our focus in this video is
4th Ventricle and the Rhomboid fossa

4th Ventricle and Rhomboid Fossa Official Links Instagram Youtube Jki-discord Notes & Illustrations Quizzes Summary & Transcript Notes ☆ Members Only Go to PDF Notes Illustrations ☆ Members Only Go to Illustrations 12345678910 4th Ventricle and Rhomboid Fossa – QUIZ Test your understanding with 10 random multiple-choice questions from the question bank. You're in the preview mode. Note: All elements work correctly on the front end. 1 / 10 Which structure demarcates the transition to the central canal? A) Vestibular area B) Median sulcus C) Foramen of Magendie D) Obex The obex marks the transition from the 4th ventricle to the central canal. 2 / 10 Which cranial nerve nucleus lies beneath the hypoglossal trigone? A) Vestibular nucleus B) Hypoglossal nucleus C) Vagal nucleus D) Facial nucleus The hypoglossal nucleus lies beneath the hypoglossal trigone and innervates tongue muscles. 3 / 10 The striae medullares mark the boundary between which structures? A) Inferior cerebellar peduncles B) Vestibular nuclei C) Pons and medulla D) Superior cerebellar peduncles The striae medullares separate the pons and medulla on the floor of the 4th ventricle. 4 / 10 The facial colliculus is formed by fibers of which cranial nerve? A) Vagus nerve (CN X) B) Facial nerve (CN VII) C) Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) D) Trigeminal nerve (CN V) The facial colliculus is formed by fibers of the facial nerve (CN VII) looping around the abducens nucleus (CN VI). 5 / 10 Which cranial nerve nucleus is associated with facial expression? A) Hypoglossal nucleus B) Vestibular nuclei C) Facial nerve nucleus D) Cochlear nuclei The motor nucleus of the facial nerve (CN VII) controls muscles of facial expression. 6 / 10 Which cranial nerve nuclei are located in the medial eminence? A) Facial nerve nucleus B) Vagus nerve nucleus C) Glossopharyngeal nucleus D) Abducens nucleus The abducens nucleus (CN VI) is located in the medial eminence of the rhomboid fossa. 7 / 10 The lateral apertures (Foramina of Luschka) open into which structure? A) Inferior medullary velum B) Central canal C) Cerebellum D) Subarachnoid space The lateral apertures connect the 4th ventricle to the subarachnoid space. 8 / 10 Which cranial nerve nucleus is found in the vagal trigone? A) Abducens nucleus B) Spinal accessory nucleus C) Vagus nucleus D) Hypoglossal nucleus The dorsal nucleus of the vagus nerve lies in the vagal trigone and controls parasympathetic functions. 9 / 10 What is the function of the area postrema? A) Regulates heart rate B) Processes auditory input C) Controls CSF circulation D) Detects toxins and triggers vomiting The area postrema detects toxins in the blood and triggers vomiting, making it part of the circumventricular organs. 10 / 10 What is the primary function of the 4th ventricle? A) CSF circulation B) Sensory processing C) Auditory signal relay D) Motor coordination The 4th ventricle allows CSF circulation between the ventricular system and the subarachnoid space. Your score is The average score is 0% Description Ventricles in the Brain Fourth Ventricle Central Canal Aqueduct of the Midbrain Third Ventricle Interventricular Foramen Lateral Ventricles Contain Cerebrospinal Fluid Subarachnoid Space Roof of 4th Ventricle (Tegmen Ventriculi Quarti) Superior Medullary Velum (Velum Medullare Superius) Inferior Medullary Velum (Velum Medullare Inferius) Tela Choroidea Choroid Plexus Fastigium Communications of 4th Ventricle Aqueduct of Midbrain (Aquaeductus Mesencephali) Lateral Apertures / Foramina of Luschka (Apertura Laterales Ventriculi Quarti) Median Aperture / Foramen of Magendie (Apertura Mediana Ventriculi Quarti) Central Canal (Canalis Centralis) Topography of the Rhomboid Fossa (Fossa Rhomboidea) Bordered by the Superior and Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle Anatomical Structures of the Rhomboid Fossa Median Sulcus (Sulcus Medianus) Medial Eminence (Eminentia Medialis) Medullary Stria (Stria Medullares) Facial Colliculus (Colliculus Facialis) Hypoglossal Trigone (Trigonum Hypoglossi) Vagal Trigone (Trigonum N. Hypoglossi) Vestibular Area (Area Vestibularis) Locus Caeruleus Cranial Nuclei of the Rhomboid Fossa Trigeminal Nerve (N. Trigeminus) Mesencephalic Nucleus of the Trigeminal Nerve (Nucleus Mesencephalicus Nervi Trigemini) Principal Nucleus of Trigeminal Nerve (Nucleus Principalis Nervi Trigemini) Spinal Nucleus of Trigeminal Nerve (Nucleus Spinalis Nervi Trigemini) Motor Nucleus of Trigeminal Nerve (Nucleus Motorius Nervi Trigemini) Abducent Nerve (N. Abducens) Nucleus of Abducent Nerve (Nucleus N. Abducensis) Facial Nerve (N. Facialis) Motor Nucleus of Facial Nerve (Nucleus N. Facialis) Superior Salivatory Nucleus (Nucleus Salivatorius) Nucleus of the Solitary Tract (Nucleus Tractus Solitarii) Vestibulocochlear Nerve (N. Vestibulocochlearis) 2x Cochlear Nuclei (Nuclei Cochlearis) 4x Vestibular Nuclei (Nuclei Vestibularis) Glossopharyngeal Nerve (N. Glossopharyngeus) Inferior Salivatory Nucleus (Nucleus Salivatorius Inferior) Nucleus of the Solitary Tract Nucleus Ambiguus Vagus Nerve (N. Vagus) Posterior Nucleus of Vagus Nerve (Nucleus Posterior Nervi Vagi) Nucleus of the Solitary Tract Nucleus Ambiguus Accessory Nerve (N. Accessorius) Nucleus Ambiguus Spinal Nucleus of Accessory Nerve (Nucleus Spinalis Nervi Accessorii) Spinal Root Cranial Root Hypoglossal Nerve (N. Hypoglossus) Nucleus of Hypoglossal Nerve (Nucleus Nervi Hypoglossi) Quiz Included in the video and on this page. Sources used in this video: Memorix Anatomy 2nd Edition by Hudák Radovan, Kachlík David, Volný Ondřej Biorender University notes and lectures Transcript 0:03 What’s up. Meditay here. Let’s continue the anatomy of the Central Nervous System. 0:08 In this segment, we’ll cover the anatomy of the 4th Ventricle, 0:11 and then we’re going to cover the structures and the cranial nuclei of the rhomboid fossa. 0:16 So the central nervous system consists of two parts: the encephalon and the spinal cord. 0:21 The encephalon is then further divided into specific parts. 0:25 We have the brainstem, which consists of the Medulla, Pons, and the Midbrain or the 0:29 mesencephalon. We have the Cerebellum back here, then the diencephalon and the telencephalon. 0:34 Our focus in this video is going to be the space between these three structures, 0:38 called the 4th Ventricle, and the base of the 4th Ventricle, called Rhomboid Fossa. Which is here. 0:44 So in this video, we’re first going to cover all the ventricles in the brain. 0:48 Then we’re going to cover the border and the communications of the 4th Ventricle. 0:52 After that, we’re going to look at the Topography of the Rhomboid fossa. Then cover the anatomical
Pons
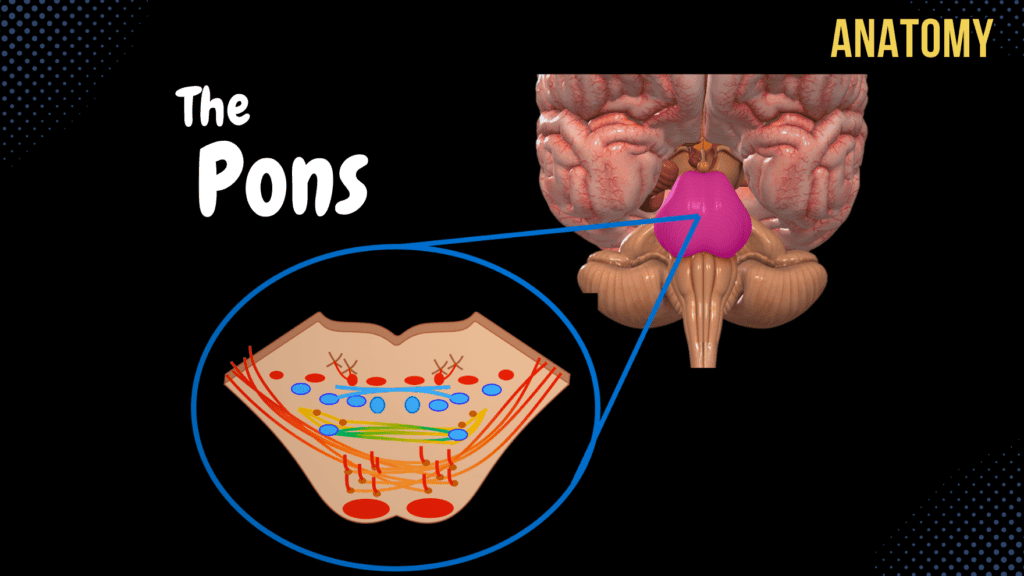
Pons – External and Internal (White & Grey matter) Official Links Instagram Youtube Jki-discord Notes & Illustrations Quizzes Summary & Transcript Notes ☆ Members Only Go to PDF Notes Illustrations ☆ Members Only Go to Illustrations 12345678910 Pons – QUIZ Test your understanding with 10 random multiple-choice questions from the question bank. You're in the preview mode. Note: All elements work correctly on the front end. 1 / 10 What is the function of the trapezoid body in the pons? A) Sound localization B) Proprioception C) Balance D) Vision The trapezoid body is part of the auditory pathway and is involved in sound localization by transmitting information to the superior olivary nucleus. 2 / 10 Which structure separates the basilar part from the tegmentum of the pons? A) Inferior cerebellar peduncle B) Trapezoid body C) Reticular formation D) Medial lemniscus The trapezoid body separates the basilar part (ventral) and the tegmentum (dorsal) of the pons and is part of the auditory pathway. 3 / 10 The reticular formation in the pons plays a role in which function? A) Sensory relay B) Motor coordination C) Vision D) Sleep and arousal The reticular formation is involved in regulating autonomic functions, arousal, and sleep-wake cycles. 4 / 10 What structure connects the pons to the cerebellum? A) Middle cerebellar peduncle B) Superior cerebellar peduncle C) Inferior cerebellar peduncle D) Medial lemniscus The middle cerebellar peduncle connects the pons to the cerebellum and is involved in motor control. 5 / 10 What is the primary function of the corticospinal tract in the pons? A) Balance B) Voluntary motor commands C) Pain transmission D) Auditory processing The corticospinal tract is part of the pyramidal system and transmits voluntary motor commands from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord. 6 / 10 What forms the posterior surface of the pons? A) Clivus B) Rhomboid fossa (floor of the fourth ventricle) C) Tentorium cerebelli D) Superior cerebellar peduncles The posterior surface of the pons contributes to the floor of the fourth ventricle and includes cerebellar peduncles. 7 / 10 What forms the medial lemniscus in the pons? A) Pontine nuclei B) Reticular formation C) Internal arcuate fibers D) Spinocerebellar fibers The medial lemniscus is formed by the decussation of the internal arcuate fibers, which carry sensory information. 8 / 10 Which cranial nerves have nuclei located in the pons? A) CN III, IV, VI, XI B) CN IX, X, XI, XII C) CN V, VI, VII, VIII D) CN I, II, VI, VII The trigeminal (V), abducens (VI), facial (VII), and vestibulocochlear (VIII) nerves have nuclei in the pons. 9 / 10 Which structure in the pons plays a role in horizontal eye movement coordination? A) Vestibulospinal tract B) Lateral lemniscus C) Tectospinal tract D) Medial longitudinal fasciculus The medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) coordinates horizontal eye movements by connecting cranial nerve nuclei. 10 / 10 What separates the basilar part and tegmentum of the pons? A) Reticular formation B) Medial lemniscus C) Inferior cerebellar peduncle D) Trapezoid body The trapezoid body, a key part of the auditory pathway, separates the ventral basilar part from the dorsal tegmentum. Your score is The average score is 0% Notes ☆ Members Only Go to PDF Notes Illustrations ☆ Members Only Go to Illustrations Notes & Illustrations Quizzes Summary & Transcript Notes ☆ Members Only Go to PDF Notes Illustrations ☆ Members Only Go to Illustrations Pons – QUIZ Test your understanding with 10 random multiple-choice questions from the question bank. Start Become a Member You have to become a member before you can access the Notes and the Quizzes. Membership Plans Description Topography of the Pons Lies above the Medulla, Below Mesencephalon, In front of the Cerebellum Anterior Surface Posterior Surface Anterior Surface of the Pons Basilar Sulcus (Sulcus Basilaris) Middle Cerebellar Peduncles (Pedunculus Cerebellaris Media) Cranial Nerve IV: Nervus Abducens between pyramid and pons Between olives and middle cerebellar peduncles Cranial Nerve VII: Facialis Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlearis Surface of Pons: Cranial Nerve V (Trigeminus) Posterior View of Pons Rhomboid Fossa (Fossa Rhomboidea) Cerebellar Peduncles (Pedunculi Cerebelli) Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Superior Cerebellar Peduncle Internal Surface of Pons Cochlear Nerve forms Trapezoid Body (Corpus Trapezoideum) Dorsal Part: Tegmentum of Pons Ventral Part: Basilar Part Gray Matter in Basilar Part of Pons Pontine Nuclei (Nuclei Pontis) For Frontopontine Tract PontoCerebellar Tract (Transverse Pontine Fibers) Cerebellorubral Tract Rubrospinal Tract Gray Matter in Tegmentum of Pons Reticular Formation (Formatio Reticularis) Nuclei of Trapezoid Body (Nuclei Corporis Trapezoideum) Nuclei of the Rhomboid Fossa (Cranial nuclei of X-XII) White Matter of Basilar Part of Pons Pontocerebellar Tract (Transverse Pontine Fibers) Coming from Corticopontine tract Frontopontine Tract Parietopontine Tract Temporopontine Tract Occipitopontine Tract Corticospinal Tract (Tractus Corticospinalis) Corticonuclear Tract (Corticobulbar tract) White Matter in Tegmentum of Pons Ascending Tracts Medial Lemniscus (Lemniscus Medialis) Gracile Fascicle (Fasciculus Gracilis) to Gracile Nucleus Cuneate Fascicle (Fasciculus Cuneatus) to Cuneate Nucleus Medial Lemniscus is formed through Internal Arcuate Fibers (Fibrae Arcuatae Internae) Epicritic Sensibility (Proprioception and Mechanoreception) Spinal Lemniscus (Lemniscus Spinalis) Anterior Spinothalamic Tract (Tractus Spinothalamicus Anterior) Lateral Spinothalamic Tract (Tractus Spinothalamicus Lateralis) Trigeminal Lemniscus (Lemniscus Trigeminalis) Anterior Spinocerebellar Tract (Tractus Spinocerebellaris Anterior) Lateral Lemniscus (Lemniscus Lateralis) From Cochlear Nerve Descending Tracts Vestibulospinal Tract (Tractus Vestibulospinalis) Rubrospinal Tract (Tractus Rubrospinalis) Tectospinal Tract (Tractus Tectospinalis) Reticulospinal Tract (Tractus Reticulospinalis) Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus (Fasciculus Longitudinalis Medialis) QUIZ Sources used in this video: Memorix Anatomy 2nd Edition by Hudák Radovan, Kachlík David, Volný Ondřej Biorender University notes and lectures Transcript 0:03What’s up, Meditay here; let’s continue the anatomy of the Central Nervous System.0:07In this segment, we’ll cover the complete anatomy of Pons0:11So the central nervous system consists of two parts:0:14the encephalon and the spinal cord. The encephalon is then further divided into specific parts.0:20We have the brainstem, which consists of the Medulla, Pons, and the Midbrain or the0:24mesencephalon. We have the Cerebellum back here, then the diencephalon and the telencephalon.0:29Our focus in this video is going to be Pons, which is here.0:33So in this video,
Medulla Oblongata
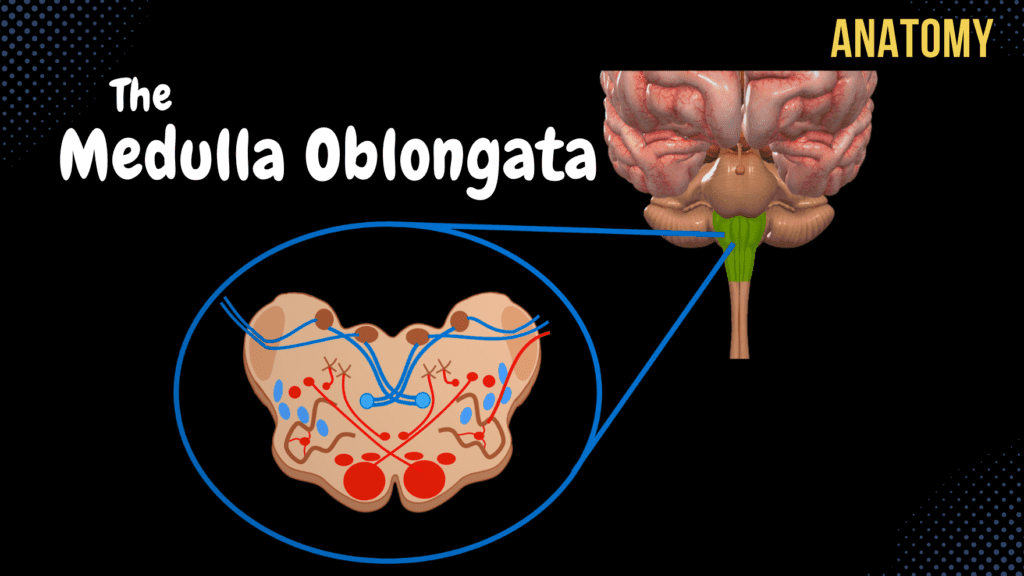
Medulla Oblongata – External & Internal (White & Grey matter) Official Links Instagram Youtube Jki-discord Notes & Illustrations Quizzes Summary & Transcript Notes ☆ Members Only Go to PDF Notes Illustrations ☆ Members Only Go to Illustrations 12345678910 Medulla Oblongata – QUIZ Test your understanding with 10 random multiple-choice questions from the question bank. You're in the preview mode. Note: All elements work correctly on the front end. 1 / 10 Which structure separates the gracile and cuneate fasciculi on the posterior medulla? A) Posterolateral sulcus B) Posterior median sulcus C) Anterior median fissure D) Inferior cerebellar peduncle The posterior intermediate sulcus lies between the gracile and cuneate fasciculi. 2 / 10 What is the anatomical landmark on the dorsal surface of the medulla between the cuneate tubercles? A) Gracile fasciculus B) Olives C) Pyramids D) Anterior median fissure The posterior median sulcus separates the gracile tubercles medially. 3 / 10 Where do fibers of the gracile and cuneate fasciculi synapse? A) Vestibular nucleus B) Inferior olivary nucleus C) Nucleus ambiguus D) Spinal trigeminal nucleus They synapse in their respective nuclei, gracile and cuneate. 4 / 10 Where does the medial lemniscus transmit sensory signals after decussation? A) Primary motor cortex B) Visual cortex C) Cerebellum D) Spinal cord It transmits signals to the thalamus for further processing. 5 / 10 Which structure in the medulla is responsible for decussating sensory fibers? A) Spinothalamic tract B) Olives C) Pyramids D) Vestibular nuclei The medial lemniscus is formed after internal arcuate fibers decussate. 6 / 10 Which nuclei are found in the rhomboid fossa of the medulla? A) IX, X B) VII, VIII C) III, IV D) V, VI The cranial nerve nuclei for X, XI, and XII are located in the rhomboid fossa. 7 / 10 Which ascending tract transmits pain and temperature signals in the medulla? A) Posterior spinocerebellar tract B) Anterior corticospinal tract C) Medial lemniscus D) Vestibulospinal tract The lateral spinothalamic tract carries pain and temperature signals. 8 / 10 Which tract transmits proprioceptive signals to the cerebellum through the medulla? A) Lateral corticospinal tract B) Tectospinal tract C) Anterior spinothalamic tract D) Rubrospinal tract The posterior spinocerebellar tract carries proprioceptive signals to the cerebellum. 9 / 10 What is the primary function of the nucleus ambiguus? A) Sensory transmission B) Balance and coordination C) Proprioception D) Reflex integration It provides motor innervation to the pharynx, larynx, and soft palate. 10 / 10 Which cranial nerve exits at the level of the pyramids? A) Vagus nerve B) Accessory nerve C) Glossopharyngeal nerve D) Trigeminal nerve The hypoglossal nerve exits at the level of the pyramids. Your score is The average score is 0% Notes ☆ Members Only Go to PDF Notes Illustrations ☆ Members Only Go to Illustrations Notes & Illustrations Quizzes Summary & Transcript Notes ☆ Members Only Go to PDF Notes Illustrations ☆ Members Only Go to Illustrations Medulla Oblongata – QUIZ Test your understanding with 10 random multiple-choice questions from the question bank. Start Become a Member You have to become a member before you can access the Notes and the Quizzes. Membership Plans Description Topography of the Medulla Oblongata: Lies above the Spinal Cord, Below Pons, In front of the Cerebellum, on Clivus, above Foramen Magnum 2.5 cm length Anterior Surface Posterior Surface Anterior Surface of the Medulla Oblongata: Anterior Median Fissure (Fissura Mediana Anterior) Right Anterolateral Sulcus (Sulcus Anterolateralis Dexter) Left Anterolateral Sulcus (Sulcus Anterolateralis Sinister) Right Posterolateral Sulcus (Sulcus Posterolateralis Dexter) Left Posterolateral Sulcus (Sulcus Posterolateralis Sinister) Pyramids of the Medulla Oblongata (Pyramis Medullae Oblongatae) Contain Decussation of Pyramid (Decussation Pyramidum) Olives of the Medulla (Oliva) Cranial Nerve XII (Hypoglossal Nerve) from Anterolateral Sulci Cranial Nerve IX (Glossopharyngeal Nerve) Cranial Nerve X (Vagus Nerve) Cranial Nerve XI (Accessory Nerve) Posterior View of Medulla Oblongata: Posterior Median Sulcus (Sulcus Medianus Posterior) Gracile Fascicle (Fasciculus Gracilis) Gracile Tubercle (Tuberculum Gracilis) Cuneate Fascicle (Fasciculus Cuneatus) Cuneate Tubercle (Tuberculum Cuneatus) Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle (Pedunculus Cerebellaris Inferior) Gray Matter of Medulla: Gracile Nucleus (Nucleus Gracilis) Cuneate Nucleus (Nucleus Cuneatus) Reticular Formation (Formatio Reticularis) Olivary Nuclei (Nuclei Olivares) Nuclei of the Rhomboid Fossa (Cranial nuclei of IX-XII) Ascending Tracts of Medulla: Gracile Fascicle (Fasciculus Gracilis) to Gracile Nucleus Epicritic Sensibility (Proprioception and Mechanoreceptors) Cuneate Fascicle (Fasciculus Cuneatus) to Cuneate Nucleus External Arcuate Fibers (Fibrae Arcuatae Externae) Internal Arcuate Fibers (Fibrae Arcuatae Internae) Decussation of the Lemnisci (Decussatio Lemnisci Medialis) Medial Lemniscus (Lemniscus Medialis) Anterior Spinocerebellar Tract (Tractus Spinocerebellaris Anterior) Through Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle Posterior Spinocerebellar Tract (Tractus Spinocerebellaris Posterior) Through Superior Cerebellar Peduncle Anterior Spinothalamic Tract (Tractus Spinothalamicus Anterior) Lateral Spinothalamic Tract (Tractus Spinothalamicus Lateralis) Descending Tracts of the Medulla: Corticospinal Tract (Tractus Corticospinalis) Decussation of Pyramids (Decussatio Pyramidum) Lateral Corticospinal Tract Anterior Corticospinal Tract Corticonuclear Tract (Corticobulbar Tract) Vestibulospinal Tract (Tractus Vestibulospinalis) Olivospinal Tract (Tractus Olivospinalis) Olivocerebellar Tract (Tractus Olivocerebellaris) Rubrospinal Tract (Tractus Rubrospinalis) Tectospinal Tract (Tractus Tectospinalis) Lateral Reticulospinal Tract (Tractus Reticulospinalis Lateralis) Medial Reticulospinal Tract (Tractus Reticulospinalis Medialis) Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus (Fasciculus Longitudinalis Medialis) QUIZ Sources used in this video: Memorix Anatomy 2nd Edition by Hudák Radovan, Kachlík David, Volný Ondřej Biorender University notes and lectures Transcript Introduction 0:03 What’s up. Meditay Here. Let’s continue the anatomy of the Central Nervous System. 0:08 In this segment, we’ll cover the complete anatomy of the medulla oblongata. 0:12 So remember, the central nervous system consists of two parts: 0:15 the encephalon and the spinal cord. The encephalon is then further divided into specific parts. 0:21 We have the brainstem, which consists of the medulla, pons, and the midbrain or the 0:25 mesencephalon. We have the cerebellum back here, then the diencephalon and the telencephalon. 0:31 Our focus in this video is going to be the medulla oblongata, which is here. 0:35 So in this video, we’re first going to cover the external surfaces of the medulla. Basically, 0:40 look at its topography and what structures you’ll find from an anterior view and a posterior view. 0:45 Then we’re gonna slice up the medulla
Internal Spinal Cord
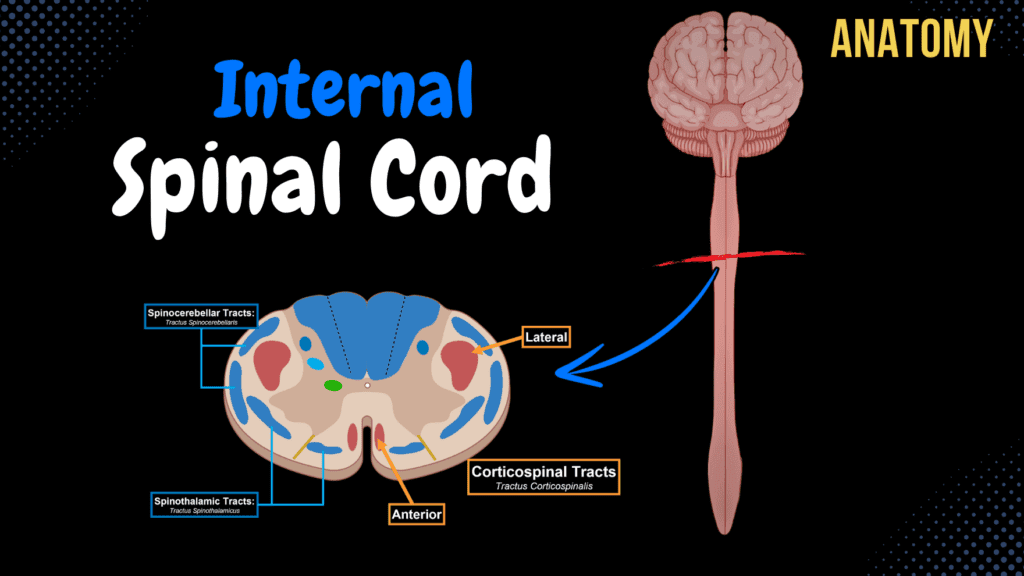
Internal Spinal Cord (Gray Matter, White Matter, Funiculus) Official Links Instagram Youtube Jki-discord Notes & Illustrations Quizzes Summary & Transcript Notes ☆ Members Only Go to PDF Notes Illustrations ☆ Members Only Go to Illustrations 12345678910 Internal Spinal Cord – QUIZ Test your understanding with 10 random multiple-choice questions from the question bank. You're in the preview mode. Note: All elements work correctly on the front end. 1 / 10 What is the function of the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF)? A) Pain Modulation B) Eye and Head Coordination C) Motor Output D) Reflex Coordination The MLF coordinates eye and head movements by connecting vestibular nuclei with ocular and cervical motor nuclei. 2 / 10 What is the primary function of the rubrospinal tract? A) Reflex Control B) Pain Transmission C) Proprioception D) Fine Motor Coordination The rubrospinal tract is involved in motor coordination, particularly fine motor movements of the upper limbs. 3 / 10 What type of fibers are found in the anterior horn of the spinal cord? A) Sensory Fibers B) Parasympathetic Fibers C) Motor Fibers D) Sympathetic Fibers The anterior horn contains motor (efferent) fibers that control skeletal muscle. 4 / 10 What is the main function of the cuneate fascicle? A) Fine Touch and Proprioception B) Reflex Control C) Motor Coordination D) Pain and Temperature The cuneate fascicle transmits sensory signals for fine touch, vibration, and conscious proprioception from the upper body. 5 / 10 Which fibers primarily occupy the lateral funiculus? A) Sensory Only B) Reflex Pathways C) Motor Only D) Sensory and Motor Fibers The lateral funiculus contains both ascending sensory tracts and descending motor tracts. 6 / 10 Which tract transmits conscious proprioception from the lower limbs? A) Rubrospinal Tract B) Gracile Fascicle C) Cuneate Fascicle D) Lateral Spinothalamic Tract The gracile fascicle transmits conscious proprioception, vibration, and fine touch from the lower limbs. 7 / 10 Which tracts are found in the posterior funiculus? A) Tectospinal and Rubrospinal Tracts B) Lateral Corticospinal Tracts C) Cuneate and Gracile Fasciculi D) Anterior Spinothalamic Tract The posterior funiculus contains the cuneate and gracile fasciculi, which carry sensory signals for fine touch and proprioception. 8 / 10 Which gray matter region contains sympathetic preganglionic neurons? A) Nucleus Proprius B) Marginal Nucleus C) Intermediolateral Nucleus D) Sacral Parasympathetic Nuclei The intermediolateral nucleus in the lateral horn contains sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the thoracic and lumbar regions. 9 / 10 Which nucleus receives input from visceral sensory fibers? A) Intermediomedial Nucleus B) Gelatinous Substance C) Posterior Thoracic Nucleus D) Marginal Nucleus The intermediomedial nucleus in the intermediate column processes visceral sensory inputs. 10 / 10 What is the primary role of the vestibulospinal tract? A) Balance and Posture B) Motor Coordination C) Pain Modulation D) Reflex Arc The vestibulospinal tract maintains balance and posture by regulating muscle tone. Your score is The average score is 0% Description Internal Surface of Spinal Cord Grey Matter – Nerve Cell Bodies and Dendrites White Matter – Myelinated axons and glial cells Grey Matter of Spinal Cord Anterior Horn (Conu Anterius) Motor Nuclei Posterior Horn (Conu Posterius) Marginal Nucleus (Nucleus Marginalis) Gelatinous Substance of Rolando (Substantia Gelatinosa Rolandi) Nucleus Proprius Posterior Thoracic Nucleus (Nucleus Thoracicus Posterior) Lateral Horn (Conu Lateralis) Sympathetic and Parasympathetic fibers Intermediate Column (Columna Intermedia) Intermediomedial Nucleus (Nucleus Intermediomedialis) Intermediolateral Nucleus (Nucleus Intermediolateralis) Sacral Parasympathetic Nuclei (Nucleus Parasympathetici Sacrales) Central Zone (Zona Centralis) Central Canal (Canalis Centralis) Central Gelatinous Substance of Spinal Cord (Substantia Gelatinosa Centralis) Fasciculi Proprii Spinal Reticular Formation (Formatio Reticulatis Spinalis) White Matter of Spinal Cord Posterior Funiculus Lateral Funiculus Anterior Funiculus White Matter Arrangement Ascending Tracts / Afferent Tracts (Tractus Ascendentes s. Afferentes) Unconscious (to Cerebellum) Unconscious Proprioceptive Sensation (Posture, Joint Stability, Feedforward Control) Anterior Spinocerebellar Tract (Tractus Spinocerebellaris Anterior) Posterior Spinocerebellar Tract (Tractus Spinocerebellaris Posterior) Conscious (to Cortex) Conscious Proprioceptive Sensation (Kinesia, Joint Position, Sense of Force) Touch, Pain, Pressure, Temperature Anterior Spinothalamic Tract (Tractus Spinothalamicus Anterior) Lateral Spinothalamic Tract (Tractus Spinothalamicus Lateralis) Cuneate Fascicle (Fasciculus Cuneatus) Gracile Fascicle (Fasciculus Gracilis) Descending Tracts / Efferent Tracts (Tractus Descendens s. Efferentes) Involuntary Movements (Extrapyramidal Tracts) Balance, Body Posture, Coarse Movements Rubrospinal Tract (Tractus Rubrospinalis) Tectospinal Tract (Tractus Tectospinalis) Vestibulospinal Tract (Tractus Vestibulospinalis) Olivospinal Tract (Tractus Olivospinalis) Medial Reticulospinal Tract (Tractus Reticulospinalis Medialis) Lateral Reticulospinal Tract (Tractus Reticulospinalis Lateralis) Voluntary Movements (Pyramidal Tracts) From Pyramidal Cells of Primary Motor Cortex Anterior Corticospinal Tract (Tractus Corticospinalis Anterior) Lateral Corticospinal Tract (Tractus Corticospinalis Lateralis) Posterior Funiculus Cuneate Fascicle (Fasciculus Cuneatus) Gracile Fascicle (Fasciculus Gracilis) Epicritic Sensibility (Proprioception and Mechanoreceptors) Lateral Funiculus Anterior Spinocerebellar Tract (Tractus Spinocerebellaris Anterior) Posterior Spinocerebellar Tract (Tractus Spinocerebellaris Posterior) Lateral Spinothalamic Tract (Tractus Spinothalamicus Lateralis) Lateral Corticospinal Tract (Tractus Corticospinalis Lateralis) Rubrospinal Tract (Tractus Rubrospinalis) Lateral Reticulospinal Tract (Tractus Reticulospinalis Lateralis) Anterior Funiculus Anterior Spinothalamic Tract (Tractus Spinothalamicus Anterior) Anterior Corticospinal Tract (Tractus Corticospinalis Anterior) Tectospinal Tract (Tractus Tectospinalis) Reflexes associated with eyes and neck Vestibulospinal Tract (Tractus Vestibulospinalis) Balance and Posture Olivospinal Tract (Tractus Olivospinalis) Balance and Posture Medial Reticulospinal Tract (Tractus Reticulospinalis Medialis) Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus (Fasciculus Longitudinalis Medialis) QUIZ Sources used in this video: Memorix Anatomy 2nd Edition by Hudák Radovan, Kachlík David, Volný Ondřej Biorender University notes and lectures Transcript 0:03 What’s up. Meditay Here. 0:05 Let’s talk about the anatomy of the Central Nervous System. 0:08 In this segment, we will be talking about the Internal surface of the Spinal Cord. Basically go through 0:13 everything you need to know regarding the anatomy of the tracts and nuclei within the spinal Cord. 0:18 Alright, so the Central Nervous System consists of two parts. The encephalon and the spinal Cord 0:24 So in this is video, we’re first going to go through the internal surface of the Spinal Cord 0:29 and talk about the distribution of white and grey matter within it. Then we’ll look detailed into 0:34 the anatomy of the grey matter and the anatomy of the white matter. Then at the end of this video, 0:39 I’ve made a quiz which you’ll hopefully be able to pass based
External Spinal Cord
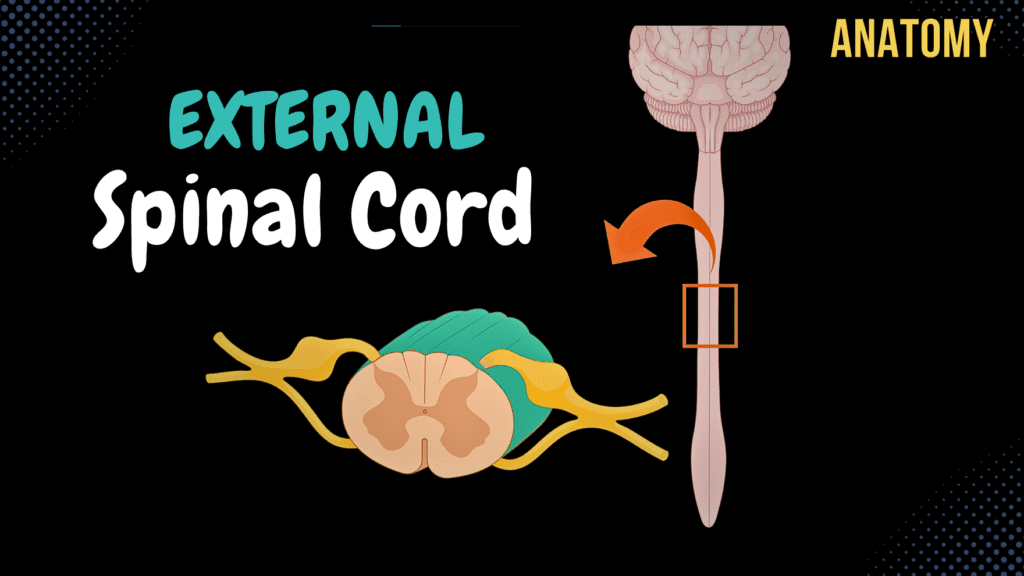
External Spinal Cord (Surface, Segments, Spinal Nerve, Enlargements, Reflex Arch) Official Links Instagram Youtube Jki-discord Notes & Illustrations Quizzes Summary & Transcript Notes ☆ Members Only Go to PDF Notes Illustrations ☆ Members Only Go to Illustrations 12345678910 External Spinal Cord – QUIZ Test your understanding with 10 random multiple-choice questions from the question bank. You're in the preview mode. Note: All elements work correctly on the front end. 1 / 10 What is the anatomical significance of the cervical enlargement? A) Brachial Plexus B) Cervical Plexus C) Lumbosacral Plexus D) Thoracic Plexus The cervical enlargement provides neural input and output for the upper limbs through the brachial plexus. 2 / 10 How many cervical segments are there in the spinal cord? A) 7 B) 6 C) 8 D) 9 There are 8 cervical spinal cord segments, corresponding to the cervical nerves. 3 / 10 What is the name of the bundle of nerve roots extending beyond the medullary cone? A) Cauda Equina B) Spinal Ganglia C) Filum Terminale D) Medullary Cone The cauda equina consists of lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal nerve roots extending beyond the medullary cone. 4 / 10 Where does the spinal cord typically terminate in adults? A) L3–L4 B) T12–L1 C) L1–L2 D) L2–L3 The spinal cord ends around the level of the L1–L2 vertebrae in adults. 5 / 10 How many spinal cord segments are there in total? A) 32 B) 30 C) 31 D) 33 The spinal cord consists of 31 segments: 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal. 6 / 10 What is the name of the canal through which the spinal cord runs? A) Central Canal B) Intervertebral Foramina C) Vertebral Canal D) Neural Canal The spinal cord runs through the vertebral canal, formed by the vertebrae. 7 / 10 What is the length of the spinal cord in adults? A) 30–35 cm B) 45–50 cm C) 40–45 cm D) 50–55 cm The spinal cord is approximately 40–45 cm long in adults, extending from the foramen magnum to the L1–L2 vertebral level. 8 / 10 Which layer of meninges provides direct vascular support to the spinal cord? A) Arachnoid Mater B) Dura Mater C) Epidural Layer D) Pia Mater The pia mater is the innermost meningeal layer that provides vascular support to the spinal cord. 9 / 10 What type of fibers are present in spinal nerves between C8 and L2? A) Sensory Fibers B) Motor Fibers C) Parasympathetic Fibers D) Sympathetic Fibers Sympathetic fibers, part of the autonomic nervous system, are present in spinal nerves between C8 and L2. 10 / 10 What is the function of the posterior median sulcus? A) Support Vasculature B) Divide the Spinal Cord Dorsally C) Conduct Motor Signals D) Conduct Reflexes The posterior median sulcus is a shallow groove that partially divides the spinal cord into left and right halves dorsally. Your score is The average score is 0% Description Topography of Spinal Cord (Medulla Spinalis) Vertebral Canal (Canalis Vertebralis) Covered by: Pia Mater Arachnoid Mater Dura Mater Foramen Magnum to L1/L2 40-45 cm long Medullary Cone (Conus Medullaris) Filum Terminale (Terminal Thread) Cauda Equina External Surface of Spinal Cord: Anterior Surface: Anterior Median Fissure (Fissura Mediana Anterior) Right Anterolateral Sulcus (Sulcus Anterolateralis Dexter) Left Anterolateral Sulcus (Sulcus Anterolateralis Sinister) Posterior Surface: Posterior Median Sulcus (Sulcus Medianus Posterior) Right Posterolateral Sulcus (Sulcus Posterolateralis Dexter) Left Posterolateral Sulcus (Sulcus Posterolateralis Sinister) Segments of the Spinal Cord 8 cervical segments 12 thoracic segments 5 lumbar segments 5 sacral segments 1 coccygeal segment Spinal nerves exit through Intervertebral Openings (Foramina Intervertebralis) Relationship between the Spinal Cord and the Vertebra: Spinous processes of cranial cervical vertebrae – Correspond to the same segment Spinous processes of caudal cervical vertebrae – Segment +1 (e.g. vertebra C7 = spinal segment C8) Spinous processes of cranial thoracic vertebrae – Segment +2 (e.g. vertebra T3 = spinal segment T5) Spinous processes of caudal thoracic vertebrae – Segment +3 Vertebrae T10–T12 – Lumbar segments L1–L4 Vertebrae T12–L1 (epiconus) – Lumbar and sacral segments L5–S2 Vertebrae L1–L2 (conus) – Sacral and single coccygeal segments S3–S5 and Co Enlargements of the Spinal Cord Cervical Enlargement (Intumenencia Cervicalis) Brachial Plexus Lumbosacral Enlargement (Intumenencia Lumbosacralis) Sacral and Lumbar Plexuses Anatomy of the Spinal Nerve: Spinal Nerves synapse with nuclei in gray matter of the spinal cord Posterior Root / Sensory Root (Radix Sensoria) Enter through the posterolateral sulci Spinal Ganglion / Dorsal Root Ganglion (Ganglion sensorium nervi spinalis) Pseudounipolar neurons Anterior Root / Motor Root (Radix Motoria) Enter through the anterolateral sulci Spinal Nerve contains: Sensory Fibers Motor Fibers Sympathetic Fibers (Between C8-L2) Parasympathetic Fibers (Between S2-S4) Branches of the Spinal Nerve: Ventral Branch Cervical Plexus Brachial Plexus Lumbar Plexus Sacral Plexus Dorsal Branch White Ramus Communicans Meningeal Branch Reflex Arch Mono-Synaptic Reflex Patellar Tendon Reflex Multi-Synaptic Reflex Withdrawal Reflex Sources used in this video: Memorix Anatomy 2nd Edition by Hudák Radovan, Kachlík David, Volný Ondřej Biorender University notes and lectures Transcript Introduction0:03What’s up. Meditay here. Let’s talk about the anatomy of the Central Nervous System.0:08In this segment, we will be talking about the external anatomy of the spinal cord.0:12basically, go through everything you need to know in regards to what the spinal cord is0:16and what you’ll find grossly on the spinal cord. Alright, so the Central Nervous System consists of0:22two parts. The encephalon, and the spinal cord. So in this is video, we’re first going0:27to go through the Topography of the Spinal cord, basically where it is,0:31where it starts and ends. Then we’ll focus on the external surface of the spinal cord,0:36basically going through all the grooves and fissures you see there. We’re also going to go0:40through the segments of the spinal cord and look at its relationship with the vertebral column.0:46Then we’ll go through the enlargements we see on the spinal cord. After that we’ll look at0:51the anatomy of a spinal nerve, and understand its 4 branches, and then quickly understand the0:56types of reflex arches we can have through the spinal cord.
Central Nervous System Overview

Central Nervous System Overview (Pars, Neurons, Neuroglia, White & Grey Matter, Development) Official Links Instagram Youtube Jki-discord Notes & Illustrations Quizzes Summary & Transcript Notes ☆ Members Only Go to PDF Notes Illustrations ☆ Members Only Go to Illustrations 12345678910 CNS Overview – QUIZ Test your understanding with 10 random multiple-choice questions from the question bank. You're in the preview mode. Note: All elements work correctly on the front end. 1 / 10 What are the three parts of the brainstem? A) Diencephalon, midbrain B) Medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain C) Telencephalon, medulla D) Cerebellum, midbrain The brainstem consists of the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain. 2 / 10 Which spinal cord region is primarily involved in autonomic functions? A) Thoracic region B) Cervical region C) Lumbar region D) Sacral region The thoracic region of the spinal cord houses autonomic nuclei for sympathetic outflow. 3 / 10 Which layer of the meninges is directly in contact with the brain? A) Pia mater B) Subarachnoid space C) Dura mater D) Arachnoid mater The pia mater is the innermost layer of the meninges, adhering closely to the brain’s surface. 4 / 10 Which neuroglia type is responsible for lining the ventricles of the brain? A) Ependymal cells B) Oligodendrocytes C) Microglia D) Astrocytes Ependymal cells line the ventricles and central canal, facilitating cerebrospinal fluid production and movement. 5 / 10 During CNS development, which vesicle forms the thalamus? A) Rhombencephalon B) Myelencephalon C) Diencephalon D) Mesencephalon The thalamus develops from the diencephalon. 6 / 10 Which structure controls basic autonomic functions like breathing and heart rate? A) Medulla oblongata B) Midbrain C) Cerebellum D) Pons The medulla oblongata controls autonomic functions such as breathing and heart rate. 7 / 10 Which type of neuron is responsible for motor output from the CNS? A) Efferent neurons B) Bipolar neurons C) Interneurons D) Afferent neurons Efferent (motor) neurons carry signals from the CNS to muscles and glands. 8 / 10 What is the primary role of astrocytes in the CNS? A) CSF production B) Immune response C) Myelination D) Blood-brain barrier Astrocytes provide mechanical support and help form the blood-brain barrier. 9 / 10 What is the role of oligodendrocytes in the CNS? A) Myelination B) Immune response C) Supporting capillaries D) Producing CSF Oligodendrocytes are responsible for forming myelin sheaths around CNS axons. 10 / 10 During which embryonic week does the CNS divide into its main vesicles? A) Week 4 B) Week 5 C) Week 6 D) Week 3 The CNS divides into its main vesicles during week 4 of embryonic development. Your score is The average score is 0% Description Central Nervous System Parts: The Brain (Encephalon) Medulla Oblongata Pons Mesencephalon Cerebellum Diencephalon Telencephalon Spinal Cord (Medulla Spinalis) Neurons: Neurons form Nerve Tissue Dendrites Cell body (nucleus) Axons Axon Terminal CNS: Oligodendrocytes PNS: Schwann Cells Myelin Sheath Histology: Granules, demarcation between axon and body Multipolar Neuron Pseudounipolar Neuron Bipolar Neuron Neuron Function: Afferent (Sensory) Nerve Interneuron Efferent (Motor) Nerve Neuroglia: Give mechanical support and provide nutrients Astrocytes form the Blood-Brain Barrier Oligodendrocytes (myelination) Microglia (Immune Cells) Ependymal Cells (Lines cavities in the brain and spinal cord) Distribution of White and Grey Matter in the CNS: Grey Matter (Rich in Nerve body and Dendrites) White Matter (Myelinated Axons) Cross Sections of the Spinal Cord Grey matter in centrum and white matter around Cross Sections of the Brain Grey matter in cortex and in the middle, white matter in between Nerve Tracts (Tractus Nervosi): Bundle of axons that connect gray matter to gray matter Classification: Association Fibers Commissural Fibers Projection Fibers Classification: Ascending Tracts Descending Tracts Indirect Tracts Development of Central Nervous System: Week 4 after fertilization Spinal Cord Rhombencephalon (Hindbrain) Mesencephalon (Midbrain) Prosencephalon (Forebrain) Week 5 after fertilization Spinal Cord Myelencephalon Metencephalon Mesencephalon (Midbrain) Diencephalon Telencephalon Sources used in this video: Memorix Anatomy 2nd Edition by Hudák Radovan, Kachlík David, Volný Ondřej Biorender University notes and lectures Transcript Introduction0:03What up. Meditay here. Let’s talk about the anatomy of the Central Nervous System.0:08In this segment, we will go through the base in understanding how the anatomy of the CNS is built.0:14And to do that, we’ll first go through the Parts of the CNS, then we’re going to go through the0:20microscopic structures of the central nervous system, basically understand what Neurons and0:23Neuroglia are and how they’re distributed in the CNS. After that, we’ll be talking about0:29the distribution of white and grey matter and talk about nerve tracts. And then end by talking0:34about the general nervous system development. Alright, so the central nervous system consistsParts of the Central Nervous System0:39of two main parts. There’s the Encephalon or the brain. And then the Spinal Cord.0:45But the brain is also divided into functionally different parts,0:49so if we look here, we have the spinal cord. And then, above the spinal cord,0:53we’ll find a structure called the brainstem And the brainstem consists of the Medulla,0:57or Medulla Oblongata, The Pons, and the Mesencephalon. Behind the brainstem,1:03we’ll find the Cerebellum, which is an essential part of the brain for muscle memory. Above that,1:08there’s the Diencephalon, which’s the area you’ll find the hypothalamus. And then we have the1:14Telencephalon, which is what we call the highest order in our brain where our personality is.1:20And so the way all of this works is that Nerves pass signals towards the higher senses of the1:25brain, then there are nerves that interpret the signals, which then generate an impulse, basically1:30activating neurons that send signals towards a muscle or an organ to activate a response.Neurons1:36And so I say neurons because that’s the primary type of cells in our Nervous System. If we take1:42a segment of the spinal cord and look at it underneath a microscope, you’ll see1:46that they’re composed of nerve tissue. And if we take a small segment of the nerve tissue,1:51you’ll find a lot of these cells we call a Neuron. Let’s talk about the neuron a little bit. Here1:57you see a simple animated neuron. They consist of Dendrites. Dendrites are what receive signals and2:03send them
