Internal Carotid Artery
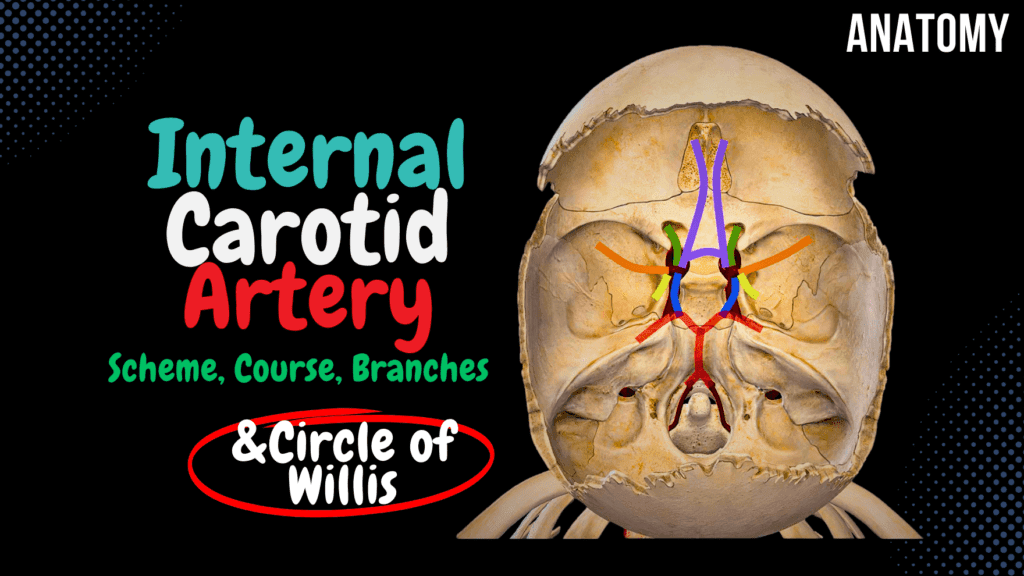
Internal Carotid Artery Scheme (Side branches, Circle of Willis) Official Links Instagram Youtube Jki-discord Notes & Illustrations Quizzes Summary & Transcript Notes ☆ Member Only Go to PDF Notes Illustrations ☆ Member Only Go to Illustrations 12345678910 Internal Carotid Artery – QUIZ Test your understanding with 10 random multiple-choice questions from the question bank. You're in the preview mode. Note: All elements work correctly on the front end. 1 / 10 Which artery forms the main blood supply to the lateral surfaces of the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes? A) Posterior cerebral artery B) Anterior cerebral artery C) Middle cerebral artery D) Ophthalmic artery The middle cerebral artery, a branch of the internal carotid artery, supplies the lateral surfaces of the brain’s hemispheres. 2 / 10 Which segment of the internal carotid artery passes through the cavernous sinus? A) Petrous segment B) Cavernous segment C) Supraclinoid segment D) Cervical segment The cavernous segment (C4) of the internal carotid artery lies within the cavernous sinus and is surrounded by cranial nerves. 3 / 10 Which segment of the internal carotid artery passes through the carotid canal? A) Cervical segment B) Cavernous segment C) Supraclinoid segment D) Petrous segment The petrous segment (C2) passes through the carotid canal, located in the temporal bone. 4 / 10 Which artery supplies the medial surface of the frontal and parietal lobes? A) Middle cerebral artery B) Anterior cerebral artery C) Anterior choroidal artery D) Posterior cerebral artery The anterior cerebral artery, a branch of the internal carotid, supplies the medial surface of the frontal and parietal lobes. 5 / 10 Which branch of the internal carotid artery supplies the retina through its central retinal branch? A) Anterior choroidal artery B) Ophthalmic artery C) Anterior cerebral artery D) Posterior communicating artery The ophthalmic artery gives rise to the central retinal artery, which supplies the retina. 6 / 10 Which clinical condition results from occlusion of the middle cerebral artery? A) Amaurosis fugax B) Contralateral hemiparesis C) Visual field defect D) Diplopia Occlusion of the middle cerebral artery can cause contralateral hemiparesis and sensory loss, often affecting the upper limb and face. 7 / 10 Which branch of the internal carotid artery participates in forming the Circle of Willis posteriorly? A) Ophthalmic artery B) Posterior communicating artery C) Anterior communicating artery D) Superior hypophyseal artery The posterior communicating artery connects the internal carotid artery to the posterior cerebral artery, forming part of the Circle of Willis. 8 / 10 Which segment of the internal carotid artery forms the carotid siphon? A) Petrous segment B) Cervical segment C) Supraclinoid segment D) Cavernous segment The cavernous segment (C4) of the internal carotid artery forms the carotid siphon. 9 / 10 Which branch of the internal carotid artery supplies the optic nerve and retina? A) Ophthalmic artery B) Posterior communicating artery C) Middle cerebral artery D) Anterior choroidal artery The ophthalmic artery, arising from the supraclinoid segment, supplies the optic nerve, retina, and orbit. 10 / 10 Which branch of the internal carotid artery contributes to the Circle of Willis? A) Posterior communicating artery B) Anterior choroidal artery C) Ophthalmic artery D) Middle cerebral artery The posterior communicating artery, a branch of the internal carotid, connects with the posterior cerebral artery. Your score is The average score is 0% Description This video covers: Parts of the Internal Carotid Canal Internal Carotid Artery and its branches: Anterior Cerebral Artery Middle Cerebral Artery Anterior Choroidal Artery Posterior Communicating Artery Blood Supply of the Brain Parts of the Internal Carotid Artery: The Internal Carotid Artery is divided into four main parts: Cervical Part Petrous Part Cavernous Part Cerebral Part Circle of Willis (Circulus Arteriosus Cerebri s. Willisi) – Thomas Willis: A critical anastomotic system at the base of the brain that ensures collateral circulation. Ophthalmic Artery Anterior Cerebral Artery Middle Cerebral Artery Anterior Choroidal Artery Posterior Communicating Artery Posterior Cerebral Artery (Branch of Basilar Artery) Cerebral Part of Internal Carotid Artery: Anterior Cerebral Artery: Runs along the longitudinal cerebral fissure. Supplies the medial surface of the frontal and parietal lobes, including: Superior Frontal Gyrus Superior Parietal Lobule Upper part of Postcentral and Precentral Gyrus Gyrus Rectus (Straight Gyrus) Middle Cerebral Artery: Clinical Note: Occlusion of this artery results in Middle Cerebral Artery Syndrome. Supplies: Insula Lentiform Nucleus Caudate Nucleus Internal Capsule Superior and Middle Temporal Gyri Large portions of the superolateral surface of the cerebral hemispheres Anterior Choroidal Artery: Runs posteriorly to form part of the choroid plexus in the lateral and third ventricles. Posterior Cerebral Artery: A branch of the basilar artery. Supplies: Occipital Lobe Inferior Temporal Gyrus Sources Used: Memorix Anatomy (2nd Edition) – Hudák Radovan, Kachlík David, Volný Ondřej. Complete Anatomy by 3D4Medical. Biorender. University Notes and Lectures. Transcript Introduction0:00alright guys so this video is about the0:02internal carotid I just want to start by0:05saying that everything you see in this0:06video was made to be schematic for you0:09to hopefully be able to visualize it now0:12essentially as the common carotid artery0:15ascends along the neck it will divide at0:17the region of the upper thyroid0:19cartilage into the external and the0:22internal carotid arteries with the0:24external carotid here in orange as we’re0:26not really going to talk about this oneParts of the Internal Carotid Artery0:28now initially the internal carotid is0:31divided into four anatomical parts0:33however in a clinical setting and this0:36really depends on the source you’re0:37studying from you may find it divided0:40into seven anatomical segments I will go0:43through the four anatomical parts but I0:45will also show you the 7-segment scheme0:48later in this video so the first part isCervical Part0:51the cervical part in the neck region0:53hence named cervical part it goes up and0:57then it goes inside the carotid canal as1:00you see here where it now becomes thePetrous Part1:03petrous part so if we take this area out1:06and visualize it a little bit you will1:09see the carotid canal here it’s1:11initially a canal within the petrous1:14part of the temporal bone so this is1:17just a coronal or a frontal section of1:20the canal now the internal carotid will1:24continue up through with the canal
External Carotid Artery
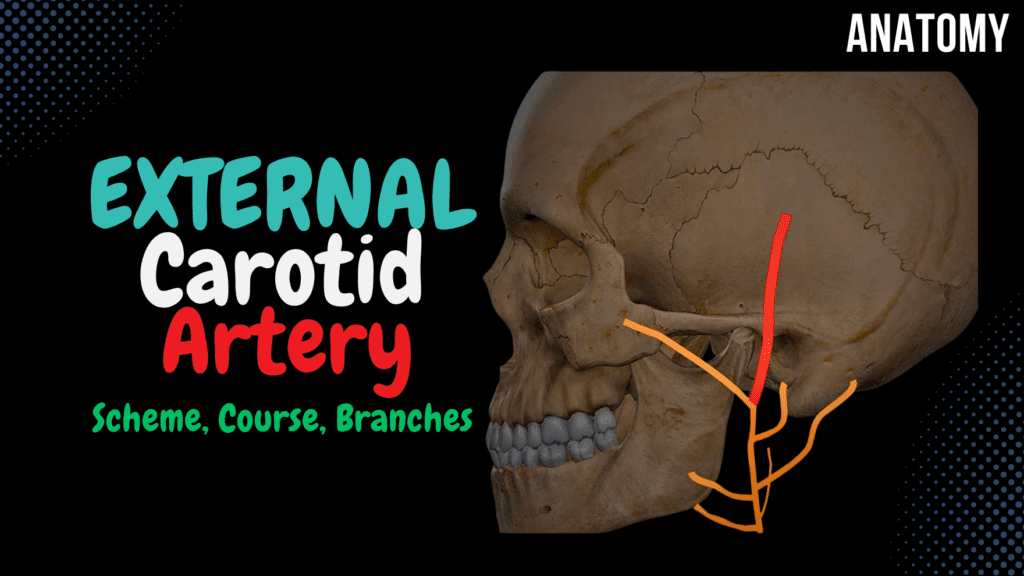
External Carotid Artery Scheme (Side branches + Mnemonics) Official Links Instagram Youtube Jki-discord Notes & Illustrations Quizzes Summary & Transcript Notes ☆ Member Only Go to PDF Notes Illustrations ☆ Member Only Go to Illustrations 12345678910 External Carotid Artery – QUIZ Test your understanding with 10 random multiple-choice questions from the question bank. You're in the preview mode. Note: All elements work correctly on the front end. 1 / 10 Which branch of the facial artery supplies the chin? A) Submental artery B) Superior thyroid artery C) Ascending pharyngeal artery D) Lingual artery The submental artery, a branch of the facial artery, supplies the chin and floor of the mouth. 2 / 10 Which branch of the external carotid artery supplies the sublingual gland? A) Lingual artery B) Superior thyroid artery C) Ascending pharyngeal artery D) Facial artery The lingual artery gives rise to the sublingual artery, which supplies the sublingual gland and floor of the mouth. 3 / 10 Which artery supplies the lateral aspect of the scalp and connects with branches of the superficial temporal artery? A) Facial artery B) Occipital artery C) Ascending pharyngeal artery D) Posterior auricular artery The posterior auricular artery supplies the lateral scalp and forms anastomoses with the superficial temporal artery. 4 / 10 Which artery supplies the medial angle of the eye via its angular branch? A) Posterior auricular artery B) Facial artery C) Lingual artery D) Maxillary artery The facial artery terminates as the angular artery, supplying the medial angle of the eye. 5 / 10 Which artery gives rise to the middle meningeal artery? A) Maxillary artery B) Ascending pharyngeal artery C) Lingual artery D) Facial artery The maxillary artery gives rise to the middle meningeal artery, which supplies the dura mater of the brain. 6 / 10 Which artery supplies the posterior aspect of the auricle? A) Superficial temporal artery B) Facial artery C) Posterior auricular artery D) Occipital artery The posterior auricular artery supplies the posterior surface of the auricle and nearby scalp. 7 / 10 Which branch of the maxillary artery enters the nasal cavity to supply the septum and lateral wall? A) Inferior alveolar artery B) Sphenopalatine artery C) Lingual artery D) Facial artery The sphenopalatine artery, a terminal branch of the maxillary artery, enters the nasal cavity to supply its septum and walls. 8 / 10 Which artery supplies the dura mater through the foramen spinosum? A) Inferior alveolar artery B) Facial artery C) Middle meningeal artery D) Occipital artery The middle meningeal artery, a branch of the maxillary artery, supplies the dura mater via the foramen spinosum. 9 / 10 Which branch of the external carotid artery passes through the mandibular foramen? A) Facial artery B) Inferior alveolar artery C) Lingual artery D) Maxillary artery The inferior alveolar artery, a branch of the maxillary artery, passes through the mandibular foramen to supply the mandible and teeth. 10 / 10 Which branch of the external carotid artery supplies the posterior cranial fossa? A) Ascending pharyngeal artery B) Occipital artery C) Superior thyroid artery D) Facial artery The ascending pharyngeal artery supplies the posterior cranial fossa, pharynx, and nearby structures. Your score is The average score is 0% Description This video covers: Anatomy of the Common Carotid Artery Anatomy of the External Carotid Artery – Course and Side Branches Blood Supply of the Teeth Blood Supply of the Nasal Cavity Common Carotid Artery: Right Common Carotid Artery originates from the Aorta. Left Common Carotid Artery originates from the Brachiocephalic trunk. Ascends without side branches. Divides at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage. Contains the Carotid Body. External Carotid Artery: Mnemonic: Some Anatomists Like Freaking Out Poor Medical Students Anterior Side Branches: Superior Thyroid Artery: Muscular branches and Superior Laryngeal Artery. Lingual Artery: Deep Lingual Artery, Dorsal Lingual Artery, Sublingual Artery. Facial Artery: Mnemonic: TAGS ALL Cervical Branches of Facial Artery (TAGS): Tonsillary Artery Ascending Facial Artery Glandular Artery Submental Artery Facial Branches of Facial Artery (ALL): Angular Artery – anastomoses with Dorsal Nasal Artery. Superior and Inferior Labial Artery. Lateral Nasal Artery. Medial Side Branches: Ascending Pharyngeal Artery: Posterior Meningeal Artery, Inferior Tympanic Artery. Posterior Side Branches: Occipital Artery: Mastoid Artery and Sternocleidomastoid Artery. Posterior Auricular Artery: Auricular Branch and Stylomastoid Artery. Terminal Branches: Maxillary Artery: Temporomandibular Joint: Deep Auricular Artery. Anterior Tympanic Artery. Middle Meningeal Artery – Superior Tympanic Branch. Clinical Note: Rupture of the Middle Meningeal Artery leads to an Epidural Hematoma, causing severe headache. Inferior Alveolar Artery – Mental Branch, Dental and Peridental Branches, Mylohyoid Branch. Infratemporal Fossa: Masseteric Artery. Anterior and Posterior Deep Temporal Artery. Pterygoid Branches. Buccal Artery. Pterygopalatine Fossa: Superior Posterior Alveolar Artery. Infraorbital Artery – Superior Alveolar Artery. Descending Palatine Artery – Lesser Palatine and Greater Palatine Artery. Sphenopalatine Artery. Artery of the Pterygopalatine Canal. Superficial Temporal Artery: Frontal Branch – anastomoses with the Supraorbital Artery of the Ophthalmic Artery. Parietal Branch – anastomoses with the Posterior Auricular Artery and the Occipital Artery. Side Branches of the Temporal Artery: Anterior Auricular. Transverse Facial Artery – supplies the Parotid Gland, Masseter Muscle, and Skin. Middle Temporal Artery. Blood Supply of the Teeth: Inferior Alveolar Artery. Superior Anterior Alveolar Artery. Superior Posterior Alveolar Artery. Blood Supply of the Nasal Cavity: Greater Palatine Artery. Sphenopalatine Artery. Anterior and Posterior Ethmoidal Arteries. Superior Labial Artery. Clinical Note: These arteries form Kisselbach’s Area (Little’s Area), which is the most common site for nosebleeds when ruptured in the nasal septum. Sources Used: Memorix Anatomy (2nd Edition) – Hudák Radovan, Kachlík David, Volný Ondřej. Complete Anatomy by 3D4Medical. Biorender. University Notes and Lectures. Transcript 1. Alright so this video is going to be about the common carotid, and the external carotid artery.So before I start, I just wanna inform that the arteries and branches this video is very schematic, but hopefully they will help you get a complete picture of this topic. I’ve also put some mneumonics along the way for you to use if you want to.2. Now – we’ll start here, looking
